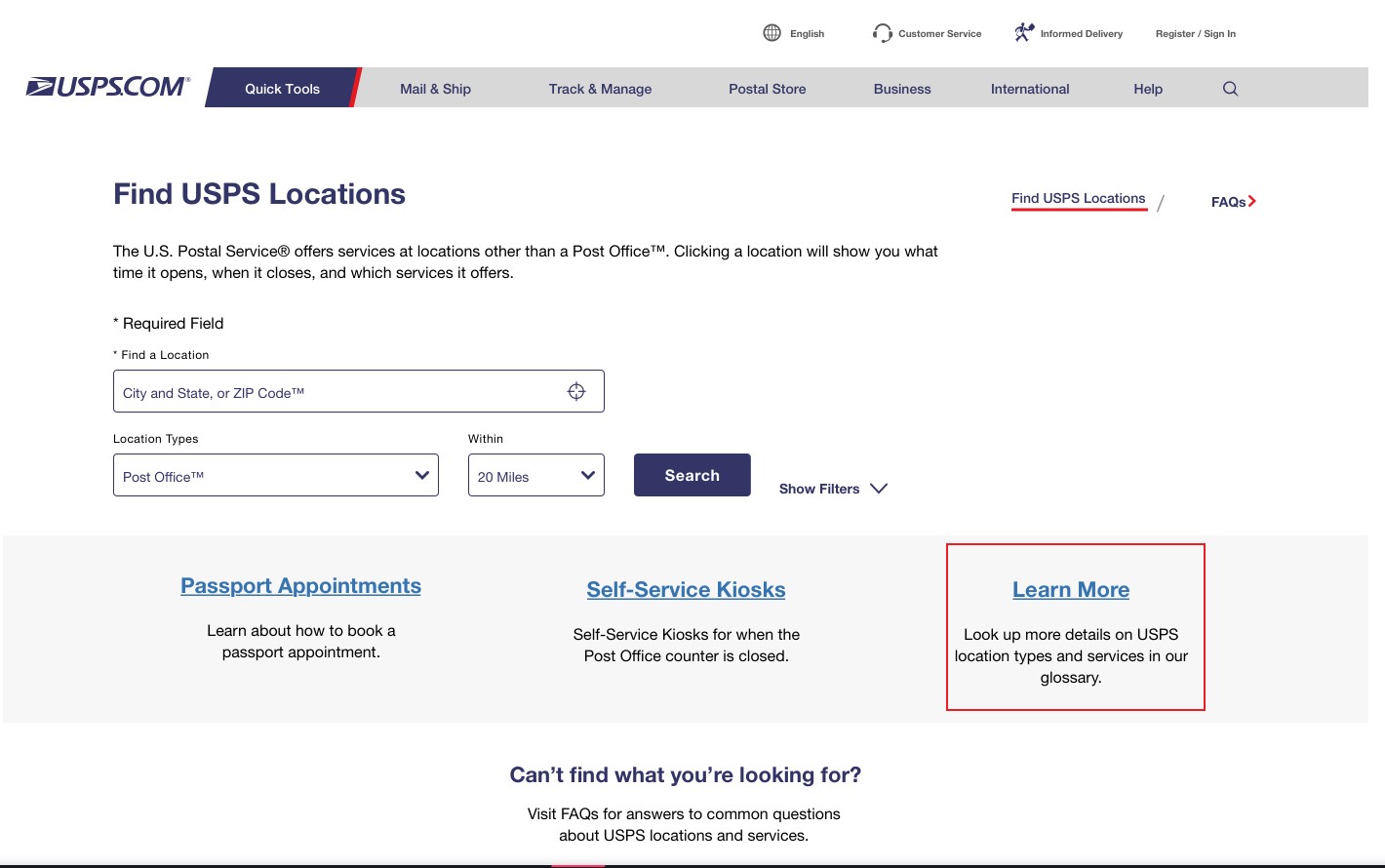
USPS, or the United States Postal Service, plays an indispensable role in the nation's communication infrastructure. Established over two centuries ago, it has evolved into one of the largest and most trusted postal services in the world. With a vast network that covers every corner of the United States, USPS delivers millions of letters and packages daily, connecting businesses, families, and communities.
As one of the oldest federal institutions, USPS has consistently adapted to changing times, embracing new technologies while maintaining its core mission of providing reliable and affordable postal services. This article will explore the history, services, challenges, and future prospects of USPS, highlighting why it remains a vital part of American life.
Whether you're a small business owner looking to ship products, a student sending out college applications, or a retiree receiving your monthly pension check, USPS touches nearly every aspect of daily life. Let's dive deeper into what makes this institution so unique and essential.
Table of Contents
- The Rich History of USPS
- Core Services Offered by USPS
- USPS Infrastructure and Network
- Financial Performance and Challenges
- Embracing Technology for Efficiency
- Competitors in the Postal Industry
- Regulatory Environment and Compliance
- Sustainability Efforts by USPS
- Enhancing Customer Experience
- The Future of USPS
The Rich History of USPS
Established in 1775 under the leadership of Benjamin Franklin, the USPS has a storied history that mirrors the growth and development of the United States. From humble beginnings as a colonial postal service to becoming a cornerstone of modern logistics, USPS has continuously expanded its reach and capabilities.
In the early days, postal routes were limited to major cities, but as the nation grew, so did the postal network. By the mid-19th century, USPS had introduced innovations such as the Pony Express and rural free delivery, ensuring that even remote areas could access postal services.
Key Milestones in USPS History
- 1775: Benjamin Franklin appointed as the first Postmaster General
- 1860: Introduction of the Pony Express
- 1970: Reorganization Act transforms USPS into an independent establishment
Today, USPS stands as the second-largest civilian employer in the country, with over 600,000 employees dedicated to delivering mail and packages.
Core Services Offered by USPS
USPS provides a wide array of services that cater to both individuals and businesses. Its core offerings include first-class mail, priority mail, express mail, and package delivery. These services are designed to meet diverse customer needs, ensuring timely and secure delivery.
Popular USPS Services
- First-Class Mail: Ideal for letters, postcards, and small packages
- Priority Mail: Offers faster delivery for heavier items
- Express Mail: Guaranteed overnight delivery within the U.S.
Additionally, USPS offers specialized services such as certified mail, registered mail, and international shipping, making it a one-stop solution for all postal needs.
USPS Infrastructure and Network
The infrastructure of USPS is vast and intricate, encompassing over 31,000 post offices and numerous processing facilities across the United States. This extensive network enables USPS to deliver mail to every address in the country, including remote and rural areas.
USPS utilizes a combination of ground and air transportation to ensure efficient delivery. With a fleet of over 200,000 vehicles, it is one of the largest civilian fleets in the world. Air transportation is used for long-distance deliveries, while ground transportation handles local and regional routes.
Key Components of USPS Infrastructure
- Post Offices: Serving as the primary point of contact for customers
- Processing Facilities: Sorting and preparing mail for delivery
- Transportation Fleet: Ensuring timely and reliable delivery
Financial Performance and Challenges
Despite its prominence, USPS faces significant financial challenges. The rise of digital communication and competition from private carriers like FedEx and UPS have impacted its revenue streams. Additionally, the requirement to pre-fund retiree health benefits has placed a substantial financial burden on the organization.
Efforts to improve financial performance include cost-cutting measures, service adjustments, and the introduction of new revenue-generating services. However, the need for legislative reform remains a critical issue that must be addressed to secure USPS's long-term viability.
Financial Highlights
- Annual Revenue: Approximately $75 billion
- Net Loss: Consistent annual deficits in recent years
- Debt: Over $100 billion in unfunded liabilities
Embracing Technology for Efficiency
USPS has made significant strides in adopting technology to enhance operational efficiency and customer experience. Advanced sorting machines, automated tracking systems, and mobile applications have streamlined processes and provided customers with real-time updates on their shipments.
In addition, USPS is exploring emerging technologies such as drones and autonomous vehicles to further optimize delivery operations. These innovations aim to reduce costs, improve service quality, and maintain USPS's competitive edge in the evolving logistics landscape.
Technological Advancements
- Automated Sorting Machines: Improves accuracy and speed
- Mobile Applications: Enables customers to track and manage shipments
- Drone Delivery: Piloting programs for remote areas
Competitors in the Postal Industry
USPS operates in a highly competitive environment, facing stiff competition from private carriers like FedEx, UPS, and DHL. These companies offer similar services but often at higher prices, targeting businesses that require premium delivery options.
Despite the competition, USPS maintains a unique advantage through its universal service obligation, which mandates delivery to every address in the country. This commitment ensures that even underserved areas receive reliable postal services, a responsibility that private carriers are not obligated to fulfill.
Key Competitors
- FedEx: Known for its express delivery services
- UPS: Offers a wide range of logistics solutions
- DHL: Specializes in international shipping
Regulatory Environment and Compliance
As a government entity, USPS operates within a complex regulatory framework. The Postal Regulatory Commission (PRC) oversees its activities, ensuring compliance with federal laws and regulations. This includes setting rates, monitoring service performance, and reviewing major operational changes.
USPS must also adhere to various labor laws, environmental regulations, and security standards. Compliance with these requirements is crucial for maintaining public trust and upholding the organization's reputation as a reliable and responsible service provider.
Regulatory Oversight
- Postal Regulatory Commission: Oversees USPS operations
- Rate Setting: Determines postage rates and fees
- Service Standards: Monitors delivery performance
Sustainability Efforts by USPS
Sustainability is a growing priority for USPS, as the organization seeks to reduce its environmental impact while maintaining efficient operations. Initiatives such as fleet modernization, energy conservation, and waste reduction are part of its broader sustainability strategy.
USPS has set ambitious goals to lower greenhouse gas emissions and improve fuel efficiency. By investing in electric vehicles and renewable energy sources, the organization aims to create a more sustainable future for postal services.
Sustainability Goals
- Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Targeting a 20% reduction by 2025
- Fleet Modernization: Transitioning to electric and hybrid vehicles
- Energy Conservation: Implementing energy-efficient practices
Enhancing Customer Experience
Customer satisfaction is a top priority for USPS, and the organization continually seeks ways to improve the customer experience. From expanding service hours to enhancing digital platforms, USPS aims to meet the evolving needs of its customers.
Feedback from customers plays a crucial role in shaping service improvements. Through surveys, focus groups, and direct communication, USPS gathers insights to refine its offerings and address customer concerns effectively.
Customer-Focused Initiatives
- Expanded Service Hours: Providing greater convenience for customers
- Enhanced Digital Platforms: Offering more features and functionality
- Customer Feedback: Driving service improvements
The Future of USPS
Looking ahead, USPS faces both challenges and opportunities. The ongoing shift toward e-commerce presents a significant growth opportunity, as more businesses rely on postal services for package delivery. However, adapting to this changing landscape requires continued investment in technology, infrastructure, and human resources.
Legislative reform remains a critical issue that could shape the future of USPS. By addressing financial challenges and modernizing operations, USPS can ensure its continued relevance and success in the years to come.
Conclusion
USPS has been a vital part of American life for over two centuries, providing reliable and affordable postal services to millions of customers. Despite financial challenges and increasing competition, USPS remains committed to fulfilling its mission of connecting people and businesses across the nation.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with USPS in the comments below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site to learn more about topics related to logistics, technology, and business. Together, let's support the continued success of this iconic institution.
![[100+] Usps Wallpapers](https://wallpapers.com/images/hd/usps-tracking-logo-atu9bv3xjtq2wbvy.jpg)
![[100+] Usps Wallpapers](https://wallpapers.com/images/hd/usps-tracking-trucks-in-a-lane-ck8f6w34vnkemfqh.jpg)