The Flemish Cap Map: A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding Its Importance And Applications
Mar 19 2025
The Flemish Cap Map has become an essential tool for researchers, marine biologists, and geographers studying the North Atlantic Ocean's underwater topography. As one of the most prominent seamounts in the region, the Flemish Cap plays a crucial role in oceanographic studies, fishing activities, and environmental conservation efforts. Understanding its geographical features, ecological significance, and historical background can provide valuable insights into marine ecosystems and climate change impacts.
The Flemish Cap Map serves as a detailed representation of this underwater plateau, offering precise information about its location, depth, and surrounding marine environments. This map is not only vital for scientific research but also for commercial fishing operations and international maritime regulations. In this article, we will explore the Flemish Cap's geography, its ecological importance, and how the map helps in understanding its complex dynamics.
With growing concerns about overfishing, climate change, and habitat destruction, the Flemish Cap Map has become increasingly relevant. It provides a visual and data-driven resource for policymakers, scientists, and stakeholders to monitor and protect this unique marine ecosystem. Let's dive deeper into the significance of this map and its applications in various fields.
Table of Contents
- Geography of the Flemish Cap
- Ecological Significance of the Flemish Cap
- Historical Background of the Flemish Cap
- Key Features of the Flemish Cap Map
- Impact on the Fishing Industry
- Environmental Conservation Efforts
- Role in Scientific Research
- Climate Change and the Flemish Cap
- Technological Advancements in Mapping
- Future Prospects and Challenges
Geography of the Flemish Cap
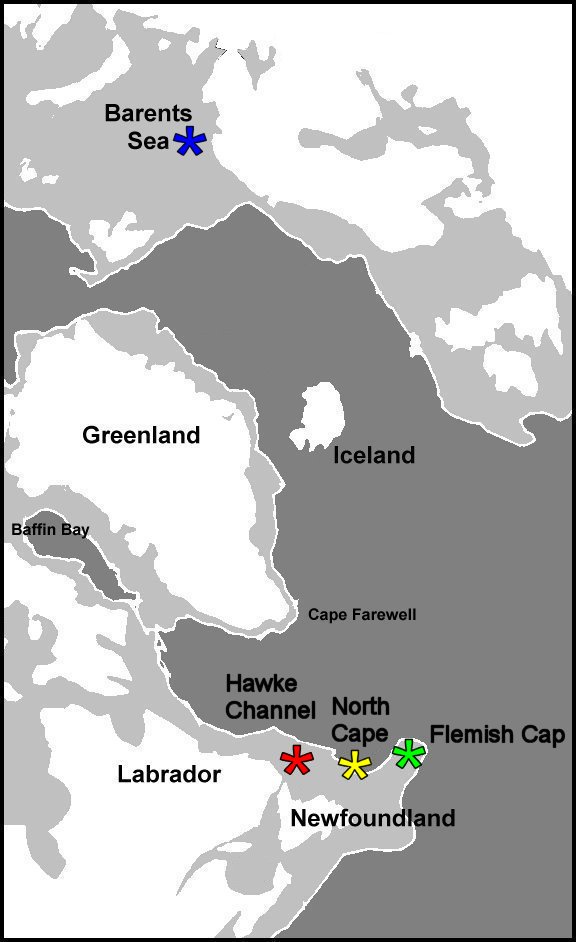
The Flemish Cap is located in the North Atlantic Ocean, approximately 600 kilometers east of Newfoundland, Canada. It is a large underwater plateau that covers an area of about 58,000 square kilometers. This section of the ocean floor rises to within 200 meters of the surface, making it an important feature for marine life and fishing activities.
Location and Dimensions
The Flemish Cap is situated between 47°N and 53°N latitude and 35°W and 45°W longitude. Its relatively shallow depth compared to the surrounding abyssal plains makes it an ideal habitat for various fish species, including cod, haddock, and redfish. The plateau's unique geography contributes to the rich biodiversity found in this region.
- Total area: 58,000 square kilometers
- Depth range: 200-600 meters
- Latitude: 47°N - 53°N
- Longitude: 35°W - 45°W
Ecological Significance of the Flemish Cap
The Flemish Cap is home to a diverse range of marine species, making it one of the most ecologically significant regions in the North Atlantic. The plateau's unique geography and oceanographic conditions create an ideal environment for fish spawning and feeding. This biodiversity supports not only local ecosystems but also global fisheries.
Key Species Found in the Flemish Cap
Several commercially important fish species inhabit the Flemish Cap, including:
- Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua)
- Redfish (Sebastes spp.)
- Haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus)
- Greenland halibut (Reinhardtius hippoglossoides)
Historical Background of the Flemish Cap
The Flemish Cap has been a vital fishing ground for centuries, attracting fishermen from Europe and North America. The name "Flemish Cap" originates from the early European explorers who noticed the similarity between the plateau's shape and the traditional Flemish hats worn in the 16th century. Over time, the region's importance in global fisheries has only grown.
Early Exploration and Exploitation
During the late 15th and early 16th centuries, European explorers began mapping the Flemish Cap and its surrounding waters. The region quickly became a popular destination for fishing fleets due to its abundant fish stocks. However, overfishing in the 20th century led to significant declines in certain species, prompting international efforts to manage and conserve this valuable resource.
Key Features of the Flemish Cap Map
A detailed Flemish Cap Map provides valuable information about the region's geography, oceanography, and marine life. These maps are essential tools for researchers, policymakers, and stakeholders working to understand and protect this unique marine ecosystem.
Types of Maps Used
Various types of maps are used to study the Flemish Cap, including:
- Bathymetric maps showing depth contours and underwater topography
- Biological maps illustrating species distribution and abundance
- Oceanographic maps displaying currents, temperature, and salinity patterns
Impact on the Fishing Industry
The Flemish Cap plays a critical role in the global fishing industry, providing significant economic benefits to coastal communities. However, overfishing and unsustainable practices have raised concerns about the long-term viability of fish stocks in the region.
Sustainable Fishing Practices
To ensure the Flemish Cap's resources are managed responsibly, international organizations have implemented measures such as catch limits, gear restrictions, and marine protected areas. These efforts aim to balance economic interests with environmental conservation goals.
Environmental Conservation Efforts
Conserving the Flemish Cap's unique marine ecosystem requires collaboration among governments, scientists, and stakeholders. Various initiatives have been launched to protect this region's biodiversity and mitigate the impacts of climate change and human activities.
International Agreements
Several international agreements and treaties address the conservation of the Flemish Cap, including:
- The Northwest Atlantic Fisheries Organization (NAFO)
- The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
- The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
Role in Scientific Research
The Flemish Cap serves as a natural laboratory for scientists studying marine ecosystems, climate change, and oceanography. Research conducted in this region provides valuable insights into global environmental processes and helps inform conservation strategies.
Key Research Areas
Some of the main research areas focusing on the Flemish Cap include:
- Marine biodiversity and ecosystem dynamics
- Climate change impacts on fish populations
- Oceanographic processes and their role in global climate systems
Climate Change and the Flemish Cap
Climate change poses significant threats to the Flemish Cap's marine ecosystem, including rising ocean temperatures, acidification, and shifting species distributions. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing effective adaptation and mitigation strategies.
Adaptation Strategies
To address the challenges posed by climate change, scientists and policymakers are exploring various adaptation strategies, such as:
- Enhancing marine protected areas
- Improving fisheries management practices
- Supporting climate-resilient species
Technological Advancements in Mapping
Recent technological advancements have significantly improved our ability to map and study the Flemish Cap. High-resolution satellite imagery, autonomous underwater vehicles, and advanced data analysis tools have revolutionized marine research and conservation efforts.
Emerging Technologies
Some of the emerging technologies used in Flemish Cap mapping include:
- Remote sensing and satellite imagery
- Autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs)
- Machine learning and artificial intelligence for data analysis
Future Prospects and Challenges
The future of the Flemish Cap depends on our ability to balance economic, environmental, and social interests. Addressing challenges such as overfishing, climate change, and habitat destruction requires sustained commitment from all stakeholders.
Key Challenges
Some of the main challenges facing the Flemish Cap include:
- Sustainable fisheries management
- Climate change adaptation and mitigation
- Conservation of biodiversity and ecosystem health
Conclusion
The Flemish Cap Map is an invaluable tool for understanding and protecting one of the North Atlantic's most ecologically and economically significant regions. By studying its geography, ecological importance, and historical background, we can develop strategies to ensure the long-term sustainability of this vital marine ecosystem. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and insights in the comments section below and explore other articles on our website for more information on related topics.