Where Is Siberia Located: A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding Siberia's Geography, Climate, And Culture
Mar 24 2025
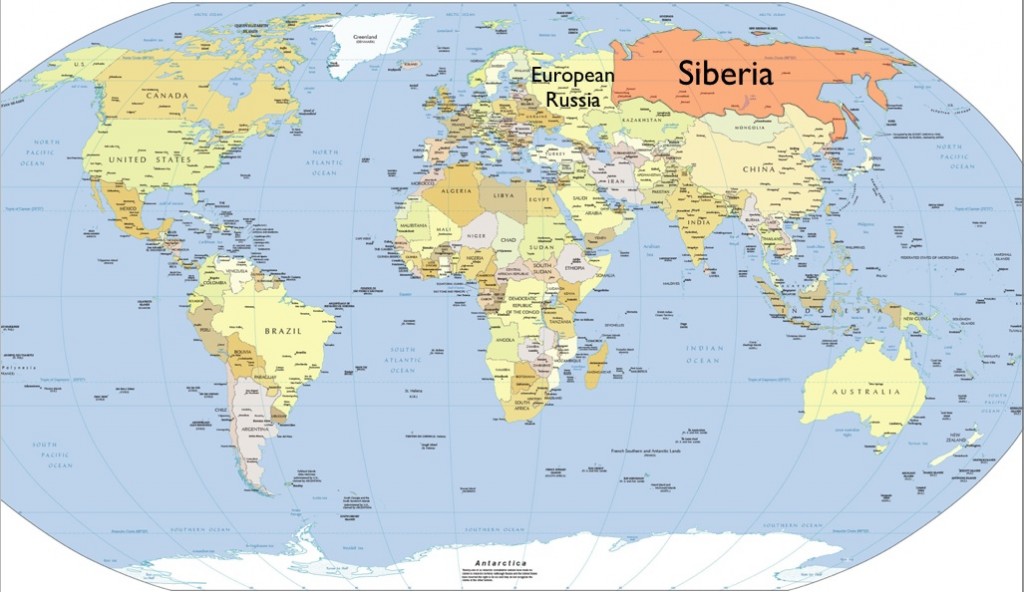
Imagine a vast, frozen land stretching endlessly across the northern part of Asia. This is Siberia, a region that captures the imagination of many with its untamed wilderness, rich history, and unique culture. If you've ever wondered, "Where is Siberia located?" this article will provide you with a detailed answer and much more. From its geographical boundaries to its significance in global geopolitics, we will explore everything you need to know about this fascinating region.
Siberia, often misunderstood as a remote and desolate area, is actually a critical part of Russia and plays a significant role in the country's economy, politics, and cultural identity. Understanding where Siberia is located is just the beginning of appreciating its importance on the world stage.
In this article, we will delve into the geography, climate, history, and culture of Siberia. By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of this vast region, its challenges, and its opportunities. Let's begin our journey into the heart of Siberia!
Table of Contents
- Where is Siberia Located?
- Geography of Siberia
- Climate in Siberia
- Historical Overview of Siberia
- Siberia's Economy
- Cultural Aspects of Siberia
- Wildlife and Nature in Siberia
- Tourism in Siberia
- Environmental Challenges in Siberia
- Conclusion
Where is Siberia Located?
Siberia is a vast region located in northern Asia, making up a significant portion of the Russian Federation. Geographically, it spans from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. To the north, it borders the Arctic Ocean, while to the south, it shares borders with Kazakhstan, Mongolia, and China. This immense area covers approximately 13.1 million square kilometers, accounting for roughly 77% of Russia's total landmass.
Key Features of Siberia's Location
- Vast expanse: Siberia covers nearly 10% of the Earth's land surface.
- Strategic position: Its location makes it a crucial link between Europe and Asia.
- Diverse landscapes: From tundra to forests and mountains, Siberia offers a wide range of natural environments.
The strategic importance of Siberia's location cannot be overstated. It serves as a bridge connecting two continents, making it a vital region for trade, transportation, and cultural exchange.
Geography of Siberia
Siberia's geography is as diverse as it is expansive. The region can be divided into several distinct zones, each with its own characteristics:
Major Landscapes in Siberia
- Tundra: Found in the northernmost parts, this area is characterized by permafrost and sparse vegetation.
- Taiga: The largest forested area in the world, covering much of central and eastern Siberia.
- Steppes: Grasslands that dominate the southern regions, ideal for agriculture and livestock.
- Mountains: The Ural Mountains in the west and the Altai Mountains in the south add to the region's topographical variety.
Siberia's geography also includes numerous rivers, lakes, and wetlands. The Ob, Yenisei, and Lena rivers are among the longest in the world, playing a crucial role in the region's ecology and economy.
Climate in Siberia
The climate of Siberia is as extreme as its geography. Known for its harsh winters, Siberia experiences temperatures that can drop below -50°C in some areas. Summers, on the other hand, can be surprisingly warm, with temperatures occasionally reaching 30°C in the southern regions.
Factors Influencing Siberia's Climate
- Latitude: Its high latitude contributes to the long, cold winters.
- Oceanic influence: Proximity to the Arctic Ocean affects weather patterns.
- Continental climate: The vast landmass results in extreme temperature variations between seasons.
Despite its challenging climate, Siberia's unique weather patterns make it a fascinating subject for climatologists and environmental scientists.
Historical Overview of Siberia
Siberia's history is rich and complex, marked by periods of exploration, colonization, and development. The region was first settled by indigenous peoples thousands of years ago. In the 16th century, Russian explorers began venturing eastward, eventually claiming Siberia as part of the Russian Empire.
Key Events in Siberia's History
- 1581: Yermak Timofeyevich leads a campaign to conquer the Siberian Khanate.
- 17th century: Russian settlers establish towns and fortresses across Siberia.
- 19th century: The Trans-Siberian Railway is constructed, facilitating trade and migration.
Siberia played a crucial role in the Soviet era, serving as a site for industrial development and forced labor camps. Today, it continues to be a vital part of Russia's national identity.
Siberia's Economy
Siberia is home to some of Russia's most important natural resources, including oil, gas, coal, and precious metals. These resources drive the region's economy and contribute significantly to the global market.
Key Economic Sectors in Siberia
- Energy: Siberia is one of the world's largest producers of oil and natural gas.
- Minerals: The region is rich in gold, diamonds, and other valuable minerals.
- Agriculture: Despite its harsh climate, Siberia produces wheat, barley, and other crops in its southern steppes.
The development of infrastructure, such as pipelines and railways, has been essential in harnessing Siberia's economic potential. However, challenges remain, including logistical difficulties and environmental concerns.
Cultural Aspects of Siberia
Siberia's culture is a blend of Russian traditions and indigenous influences. The region is home to over 40 ethnic groups, each with its own language, customs, and beliefs. This diversity enriches Siberia's cultural landscape, making it a vibrant and dynamic place.
Traditional Practices in Siberia
- Shamanism: Practiced by many indigenous groups, shamanism plays a central role in spiritual life.
- Festivals: Events like the Buryat Tsagaan Sar celebrate cultural heritage and community.
- Cuisine: Siberian cuisine features hearty dishes designed to withstand the cold climate.
Siberia's cultural richness is a testament to its resilience and adaptability in the face of harsh conditions.
Wildlife and Nature in Siberia
Siberia's vast wilderness is home to a wide variety of wildlife, from the iconic Siberian tiger to the elusive snow leopard. The region's diverse ecosystems support a rich biodiversity, making it a haven for nature enthusiasts and conservationists alike.
Endangered Species in Siberia
- Siberian tiger: Conservation efforts aim to protect this majestic predator.
- Reindeer: Indigenous populations rely on these animals for transportation and sustenance.
- Birds: Siberia is a critical stopover for migratory birds traveling between Asia and Europe.
Efforts to preserve Siberia's natural habitats are ongoing, with international organizations and local communities working together to ensure the survival of its unique flora and fauna.
Tourism in Siberia
Despite its remote location, Siberia is becoming an increasingly popular destination for adventurous travelers. From exploring the frozen landscapes of Lake Baikal to hiking in the Altai Mountains, there are countless opportunities to experience the region's natural beauty.
Top Tourist Attractions in Siberia
- Lake Baikal: The world's deepest freshwater lake offers stunning views and unique wildlife.
- Novosibirsk: As Siberia's largest city, it provides a mix of urban culture and historical landmarks.
- Trans-Siberian Railway: A journey across Siberia is an unforgettable experience.
With its growing tourism infrastructure, Siberia is poised to become a premier destination for those seeking adventure and discovery.
Environmental Challenges in Siberia
Siberia faces numerous environmental challenges, including deforestation, pollution, and climate change. The melting of permafrost, in particular, poses significant risks to infrastructure and ecosystems.
Initiatives to Protect Siberia's Environment
- Protected areas: National parks and reserves help preserve biodiversity.
- Renewable energy: Investments in wind and solar power aim to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- International cooperation: Collaborative efforts focus on addressing global climate issues.
Sustaining Siberia's environment requires a concerted effort from governments, businesses, and individuals. The region's future depends on balancing development with conservation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Siberia's location, geography, climate, history, economy, culture, wildlife, and tourism all contribute to its unique identity. Understanding where Siberia is located is just the first step in appreciating its significance. As we have explored, Siberia is a region of immense natural beauty, rich cultural heritage, and economic potential.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences about Siberia in the comments below. Have you visited this incredible region? What did you enjoy most? For more insights into the world's most fascinating places, explore our other articles. Together, let's continue to learn and grow!